Skin Cancer, Early Check, Early Treat!
2025-05-13
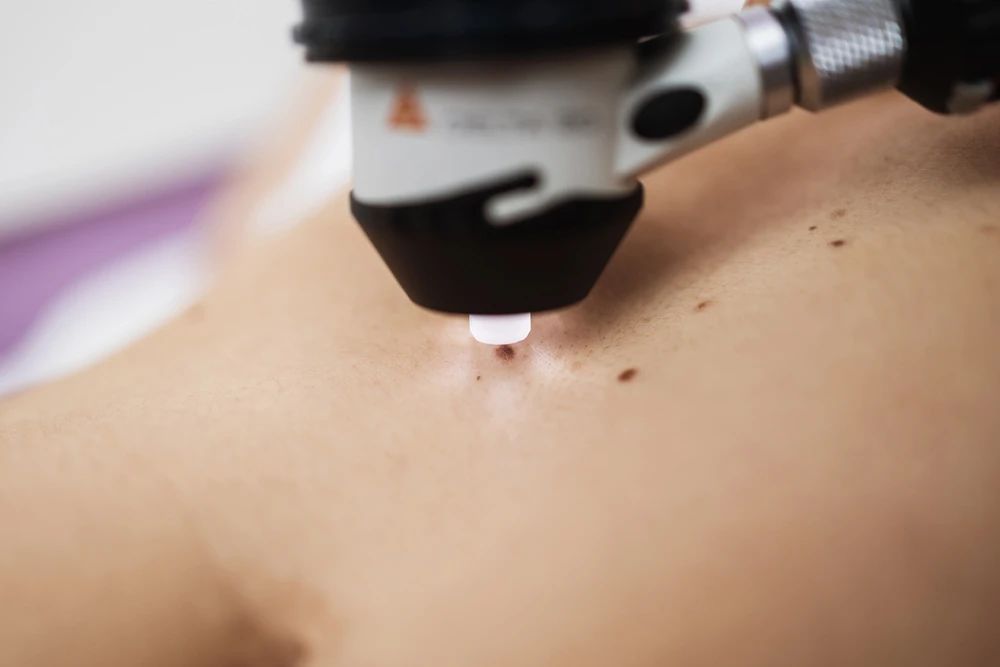
1、What is skin cancer Skin cancer, like other cancers, caused by various factors such as lifestyle habits, genetics, and infections. It often occurs in exposed areas such as the head, face, hands, and feet. When the lesion is small, it easily be mistaken for a pigmented nevus or wart, until the doctor suggests a pathological examination that it is skin cancer. According to data, white skinned people have a high probability of developing skin cancer. The proportion of Asian people suffering from skin cancer is lower, but skin problems cannot be underestimated. If we find by accident that the skin has new or increased pigmented nevus, spots, erosion, pimples or other manifestations, you need to consult a professional dermatologist as soon as possible. In addition, annual skin examination is also necessary. Early skin cancer often lacks of symptoms such as "pain" or "itching". In addition, by analyzing the size, color, shape, and other characteristics of skin lesions, it is still difficult for doctors to distinguish early skin cancer from pigmented nevi, warts, and scabs with the naked eye. At this point, dermatoscopy exam can effectively assist in diagnosis. 2、Dermoscopy Professional dermatoscopy is a new non-invasive diagnostic technique. It can magnify the skin, effectively block the reflection of light on the skin surface, and concentrate the light deeply into the skin, visualizing the color and structure of the top, middle, and bottom parts of the skin (epidermis, dermoepidermal junction, and papillary dermis). This colour and structure cannot be seen with the naked eye. Dermoscopy has been shown to significantly increase the clinical diagnosis of skin lesions and with a 30% improvement of diagnosis of melanoma compared to that achieved by clinical examination alone. In addition, dermoscopy can be used to diagnose other types of skin tumours such as basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, cylindromas, dermatofibromas, angiomas, seborrheic keratosis etc. Suspicious moles and skin lesions will be excised by a doctor for biopsy and histology. Without dermoscopy, the skin cancer detection rate was 20:1 (20 cases suspected by naked eye,find one skin cancer). Detection rate of skin cancer is 4:1 using dermoscopy (excision of 4 cases suspicious under dermatoscopy and found 1 skin cancer). The number of surgical operation and biopsy greatly reduced. 3、Utilizing mole mapping and dermoscopy A comprehensive record is established for each pigmented nevus on the entire body, serving as a unique identification profile. "Some of the pigmented nevi on the body remain the same for many years, while others change over time. How can I know if some pigmented nevi changes?" Pigmented nevus is changing, and the naked eye's ability to distinguish is very poor. Often patients have no evidence for how the lesions changing, just by their feeling. In the Dermatology of Parkway, we created the Mole-map medical service. In Mole-map, we connect a dermatoscope to a camera, take photos of each pigmented mole (or skin lesion), establish their identity file, create a location map, form an examination report, and record it on an electronic disc. In this way, each pigmented mole (or skin lesion) is equivalent to having an "ID card", with information covering size, color, shape, and location... After three months, one year, or many years, data can be retrieved at any time for comparison, and based on evidence, identification can be made, thus tracking and comparing all pigmented moles (or skin lesion). Article contributed by Dr. Li LI, Chief Physician of Dermatology at Parkway.