Frozen Shoulder: Everything You Need To Know
2022-09-02
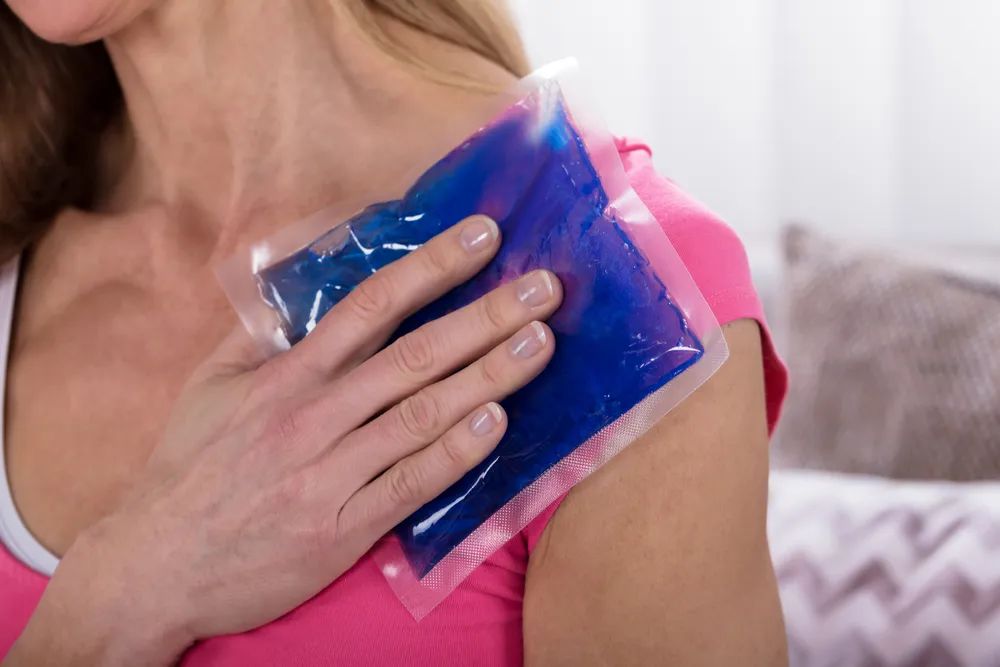
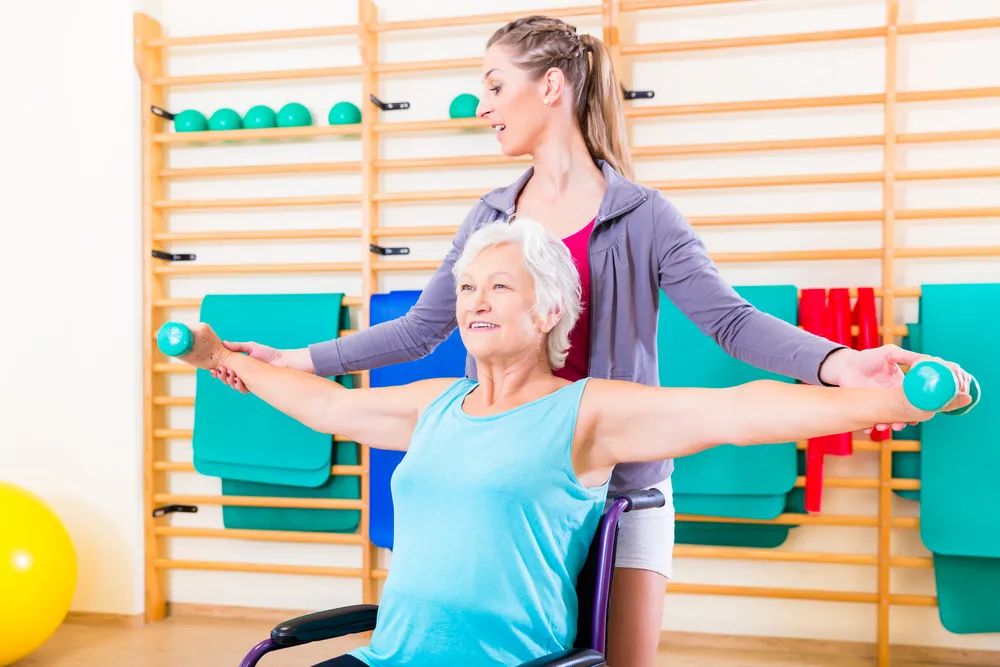
PARKWAY 百汇医疗 If you’re experiencing pain and immobility in your shoulder, it could be frozen shoulder. Here’s everything you need to know. What is frozen shoulder? Frozen shoulder is a painful condition that affects the mobility of your shoulder joint, more common in patients between the ages of 40 and 60. Also known as adhesive capsulitis, it is a result of a build-up of inflamed scar tissue in your shoulder joint that prevents proper movement. There’s also less synovial fluid to lubricate the joint, which further restricts mobility. What are the symptoms of frozen shoulder? The stages of frozen shoulder Doctors sometimes describe frozen shoulder in 3 stages. During the acute painful and freezing stage, you begin to notice pain. Stiffness of the shoulder slowly sets in as a result of the pain and the lack of movement in the shoulder. During the frozen stage, the pain intensity decreases, but the stiffness persists or worsen, and you may not be able to move the joint much at all, although the pain may improve. The final stage is the thawing stage, when you slowly regain mobility in the joint. What causes frozen shoulder? There is no clear-cut cause of frozen shoulder. Some people are more at risk than others. Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease have been linked to frozen shoulder. It is also more common in patients recovering from stroke or surgery that prevents movement of the shoulder for an extended period of time. Inactivity leads to inflammation and the development of bands of tissue called adhesions, which leads to frozen shoulder. Any injury or trauma to the area can also lead to the condition if scar tissue forms. How can frozen shoulder be diagnosed? If you experience any of the symptoms of frozen shoulder, you should visit your doctor. They can carry out a range of tests, including a general examination and a discussion about your medical history. They will also perform movement assessments. You will be asked to move your shoulder in different directions to give an indication of how restricted the joint has become. Your doctor may also order an MRI to check you haven’t torn any ligaments, or an X-ray to rule out arthritis. How can a frozen shoulder be treated? There are a few different approaches your doctor can take to treat the condition. Recalcitrant frozen shoulder can last for a few years, and hence all frozen shoulders should be treated as soon as possible. Aggressive treatment can minimize your recovery time. Over the counter anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen can help to ease pain and swelling in the joint. Steroid injections can also be used to reduce swelling and improve your range of movement. Ultrasound therapy or electric stimulation can break down scar tissue. Icing the joint can also reduce swelling. A procedure known as hydro dilatation may improve mobility. Your doctor will inject water into your shoulder to stretch the joint. Surgery is an option that is usually reserved for very severe and persistent cases. If the frozen shoulder is resistant to treatment, arthroscopic surgery can release scar tissue around the joint. Manipulating the joint under anesthesia is another technique that is used but it carries a risk of fracturing the arm. For this reason, manipulation is often done in conjunction with arthroscopic surgery nowadays. Exercise for recovery Physical therapy can also improve your range of motion. Frozen shoulder usually originates due to inactivity, so an exercise program can counteract this. Your doctor will refer you to a physical therapist who will give you a number of exercises to both stretch and strengthen the joint. It’s important not to push yourself too hard, but gentle circular, up-and-down and side-to-side movements followed by icing the joint usually gets results. You should not do anything too strenuous like lifting heavy objects or playing contact sports. Physical therapy is the most common treatment for a frozen shoulder, but it does take time. Recovery Recovering from a frozen shoulder is a lengthy process. There are instances where mobility is permanently affected, but in most cases patients recover within 6 months to 1 year. Early intervention and regular physical therapy will play a part in decreasing the length of your rehabilitation period. How can a frozen shoulder be prevented? Whilst the exact cause of frozen shoulder is difficult to pinpoint, inactivity is a trigger. You should always keep the joint mobile and exercise regularly. If you are injured or unwell and unable to move, talk to your doctor about joint health during this time. Eat a balanced diet and if you have diabetes, ensure your condition is under control. If you think you have frozen shoulder You should visit your doctor as soon as possible. Early intervention and proper management of the condition will give you the best chance of a quick recovery. Article reviewed by Dr. David Jiang,Orthopedics & Sports Medicine Surgeon. Osteopathy, etc.